MetalLB Operator
TOC
Understanding MetalLB Operator
The MetalLB Operator provides a Kubernetes-native load balancer implementation for on-premises or bare-metal environments that do not have access to cloud load balancer services. It allows Service resources of type LoadBalancer to function by assigning external IP addresses to services and advertising those addresses via Layer 2 (ARP/NDP) or Layer 3 (BGP).
The Operator automates the lifecycle management of MetalLB components, including installation, upgrades, and configuration synchronization.
Terminology
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| VIP | A Virtual IP Address (VIP) is the IP address assigned by MetalLB for the LoadBalancer type internal routing, providing a unified access point for external traffic to access services within the cluster. |
| ARP | The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is utilized to map network layer IP addresses to data link layer MAC addresses. |
| GARP | Gratuitous ARP (GARP) is a special ARP request used to inform other nodes in the network about the binding of an IP address to a MAC address. Unlike normal ARP requests, GARP does not wait for responses but actively sends information across the network. |
| ARP Responder | A component of MetalLB responsible for responding to ARP requests by mapping the VIP to the node's MAC address. When a node needs to communicate with the VIP, it sends ARP requests to retrieve the MAC address corresponding to the VIP. Each available node has an ARP Responder that responds to these requests, mapping the VIP to the node's MAC address. |
| Controller | A component of MetalLB that dynamically allocates VIPs from the external address pool for LoadBalancer type internal routing. The Controller listens for creation and deletion events of internal routes in the cluster to allocate or free VIPs as required. |
| Speaker | A component of MetalLB that determines, based on policies or algorithms, whether nodes should host a VIP and send GARP. It ensures a certain level of balance among nodes, and when a node becomes unavailable, other nodes can take over the VIP and send GARP, thereby achieving high availability. |
Principles of High Availability in MetalLB
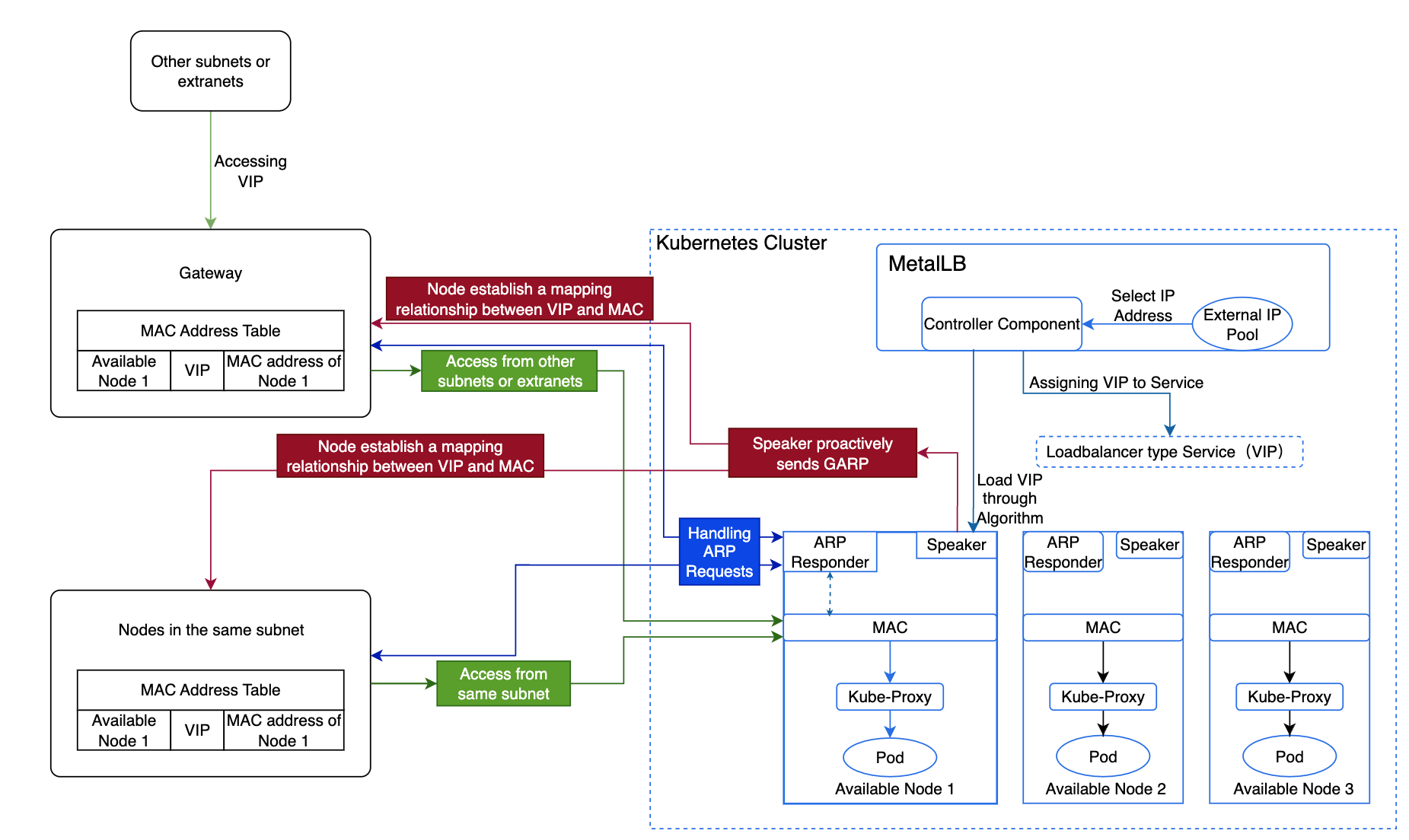
By default, the platform uses MetalLB's ARP mode, and the specific implementation process and principles are as follows:
-
The Controller component of MetalLB selects an IP address from the external address pool and allocates it to the LoadBalancer type internal routing as a VIP.
-
MetalLB selects an available node as the leader to host the VIP based on the algorithm, which then forwards the traffic.
-
The Speaker component on this node actively sends GARP, establishing a mapping relationship between the VIP and MAC address across all nodes.
-
Nodes within the same subnet, upon learning the mapping between the VIP and the available node's MAC address, will communicate directly with this node when accessing the VIP.
-
Nodes in different subnets will route traffic to the gateway of their subnet first, which will then forward the traffic to the node hosting the VIP.
-
-
When this node encounters a failure, MetalLB selects another leader to host the VIP. Then send GARP to refresh Service IP mac address, thereby ensuring high availability.
-
Upon reaching the node, Kube-Proxy forwards the traffic to the corresponding Pod.
Algorithm for Selecting VIP Host Nodes
The election of the "leader" (the node which is going to advertise the IP) of a given loadbalancer IP is stateless and works in the following way:
- each speaker collects the list of the potential announcers of a given IP, taking into account active speakers, external traffic policy, active endpoints, node selectors and other things.
- each speaker does the same computation: it gets a sorted list of a hash of "node+VIP" elements and announces the service if it is the first item of the list.
This removes the need of having to keep memory of which speaker is in charge of announcing a given IP.
Calculation Formula
The formula is: Number of external address pools = ceil(n-vip / n-node), where ceil rounds up.
Note: If using virtual machines, the number of virtual machines = Number of external address pools * n. Here, n must be greater than 2, with a maximum of one node failure allowed.
-
n-vip: Represents the number of VIPs.
-
n-node: Represents the number of VIPs a single node can handle.
Application Example
If a company has 10 VIPs, and each available node can handle 5 VIPs, allowing for one node failure, how should the company plan the number of external address pools and available nodes?
Analysis:
A total of two external address pools and four available nodes are needed.
-
Each available node can handle a maximum of 5 VIPs, meaning one external address pool can accommodate 5 VIPs, so two external address pools are required for 10 VIPs.
-
Allowing one node failure means that each address pool must include one node hosting the VIP and one backup node, resulting in two available nodes for each of the two external address pools.
Custom Resource Definitions
The MetalLB Operator installs and manages several CRDs under the metallb.io API group. These CRDs define how MetalLB assigns and advertises IP addresses.
| CRD | Kind | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
IPAddressPool | IPAddressPool | Defines the pool of IP addresses available for load balancer services. |
L2Advertisement | L2Advertisement | Configures how IPs from pools are advertised using ARP/NDP (Layer 2). |
BGPPeer | BGPPeer | Defines a BGP peer for MetalLB to establish routing sessions (Layer 3). |
BGPAdvertisement | BGPAdvertisement | Specifies which IPAddressPools are advertised over BGP and with what policies. |
BFDProfile | BFDProfile | Optional; defines Bidirectional Forwarding Detection parameters for faster BGP failure detection. |
IPAddressPool
Defines the range(s) of IPs MetalLB can assign to Service.type=LoadBalancer.
- One or more CIDRs or ranges.
- By default, MetalLB will allocate IPs from any configured address pool with free addresses. This might end up using “expensive” addresses for services that don't require it.
To prevent this behaviour you can disable automatic allocation for a pool by setting the autoAssign flag to
false
L2Advertisement
Used in Layer 2 mode, where MetalLB announces the IP via ARP/NDP.
- List of pools whose IPs will be advertised.
BGPPeer
- IP address of the peer router.
- ASN of the peer.
- ASN used by MetalLB.
holdTime/keepaliveTime: Optional timers for BGP sessions.- You can limit peers to certain nodes by using the node-selectors attribute of peers in the configuration.
BGPAdvertisement
Controls how IPs from pools are advertised over BGP.
- Which pools to advertise.
- Route aggregation prefix length.
- BGP community attributes.
BFDProfile (optional)
Used to define BFD (Bidirectional Forwarding Detection) parameters for BGP peers.
Constraints and Limitations
The IP resources for the external address must meet the following conditions:
-
The external address pool must be layer 2 (L2) interconnected with available nodes.
-
The IPs must be usable by the platform and cannot include IPs already in use by the physical network, such as gateway IPs.
-
There must be no overlap with the networks used by the cluster, including Cluster CIDR, Service CIDR, subnets, etc.
-
In a dual-stack environment, ensure that both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses exist simultaneously in the same external address pool, and their counts are both greater than 0. Otherwise, dual-stack LoadBalancer type internal routes will not be able to obtain external access addresses.
-
In an IPv6 environment, nodes' DNS must support IPv6; otherwise, the MetalLB plugin cannot be successfully deployed.
Installing and Uninstalling the MetalLB Operator
The Operator can be installed through Cluster Plugin in Alauda Container Platform web console.
- Navigate to
Administrator->Marketplace->Cluster Plugin - Enter the keyword
MetalLB. - Click
⋮then Install. - When installed, click
⋮then Uninstall.
Upgrade the MetalLB Operator
Upgrade MetalLB Operator through upload package in Alauda Container Platform web console.
- Navigate to
Administrator->Marketplace->Upload Package
Learn more about Upload Package.